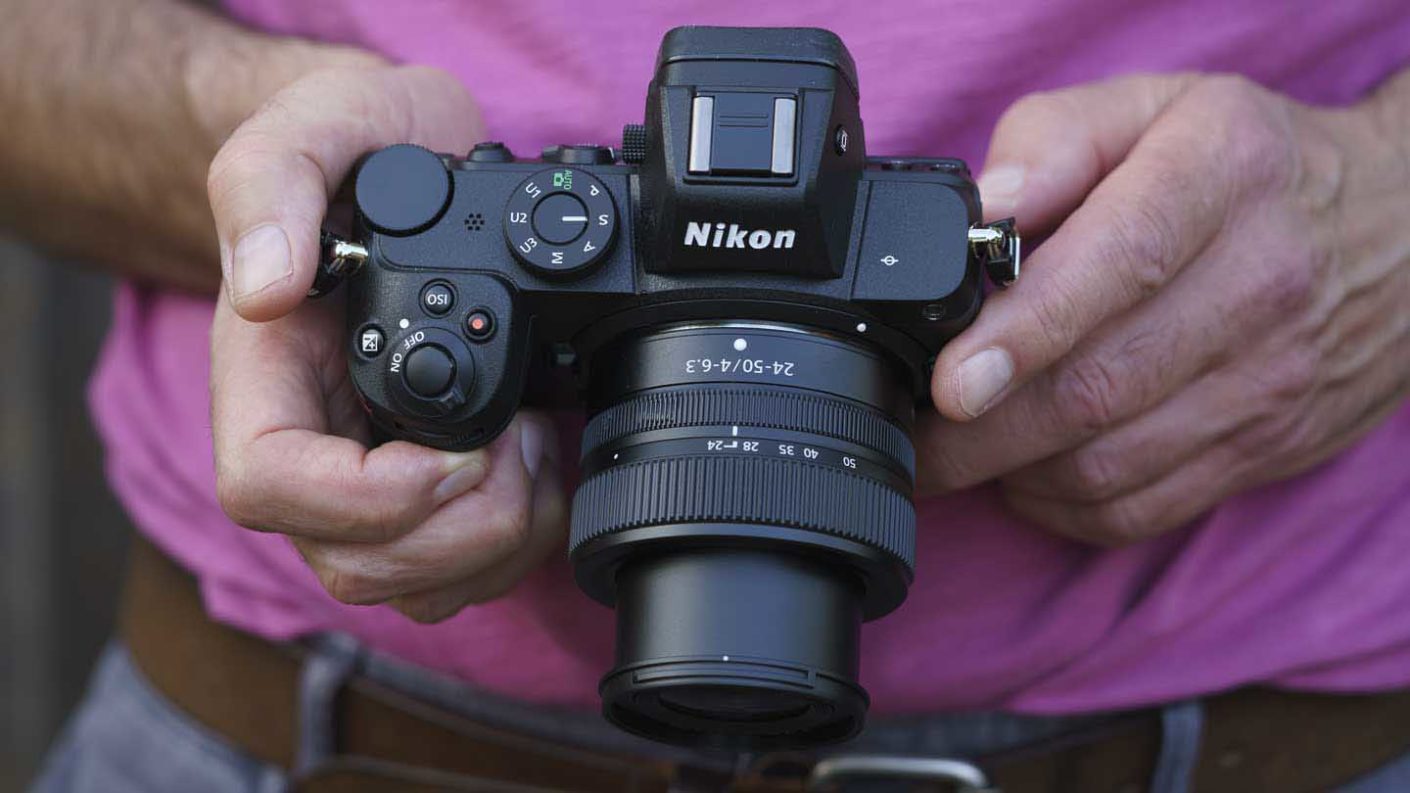
There has never been a better time to pick up photography. Photography for beginners these days not only offers the advantage of amazing consumer technology from smartphones on up to interchangeable lens cameras, but there is also now a whole internet full of resources at your disposal.
While your predecessor cut their teeth on the big, clunky, DSLRs from the early 2000s or film cameras from the decades prior, camera manufacturers today have hit their stride. No one makes a bad camera. No one.
Manufacturers have found ways to pack incredible technology into smaller bodies, streamline the menu systems and make photography for beginners so much easier than before by giving them unprecedented control over the picture-taking process – even to the point of changing your area of focus after taking an image!
What’s more, as digital cameras have improved (and the number of different camera types has expanded), they’ve come down in price quite considerably. And tech from the flagship cameras trickles down to the bottom every couple years. Nowhere do we see this more than in the entry-level camera market – particularly among the best beginner full-frame cameras. This has been perhaps the most hotly contested area of competition for the big camera manufacturers over the years, which is welcome news beginners in photography who might be on a tight budget or simply trying to decide if this is a hobby they want to pursue long-term.
In this photography for beginners guide we’re going to address two key subjects: choosing the right camera you can grow with and learning the core techniques that will help you grow. To this end, we’ll cover:
- Choosing a beginner camera
- Choosing a lens
- Understanding your camera and beginner photography techniques
And remember, sharing is caring. If you have some great insights into techniques you’ve learned over the years, please do share them in the comments down below!

Choosing a beginner camera
So what should you look for in your first camera when just getting started in photography? Naturally, price is a major concern. You don’t want to break the bank on a pro camera straightaway. You might find you don’t have the time to dedicate to photography. You might even find you don’t like it. Or – and it happens – you might find that you’re just not very good. And that’s OK! At least you didn’t spend three grand finding that out!
Many beginner cameras are priced low these days to compete, but it’s worth taking a look at the refurbished market as well. Often you can find better deals and more spec for your money buying a manufacturer refurbished model. You can even help fund your purchase by selling any old gear you may have.
Simplicity is another key factor to consider when buying an entry-level camera. You want a camera that keeps things relatively easy so that anybody venturing into photography for the first time, or upgrading from a smartphone, can get good results without lots of technical knowledge and experience.
It’s important to feel reassured when you’re just starting out, and inspired by what you can achieve. The best cameras for beginners are those that offer some room to grow. If you’re new to photography, you’ll want a camera that offers fully automatic shooting options and scene modes so that you can easily tailor your camera settings to the scene in front of you, but you’ll also want the option to take manual control over the process.
Finally, do you want a DSLR or a mirrorless camera? Though mirrorless technology is where the market is moving, the best DSLRs still offer a few advantages that really suit particular types of photography. For instance, sports and wildlife photographers might appreciate the precision of a DSLR’s phase detection autofocus. The best beginner mirrorless cameras offer bigger sensors, interchangeable lenses and superb AF systems in a much smaller body size.
It’s also worth stating something that’s true in professional photography and photography for beginners: if you can, it’s always best to get hands-on with a camera before buying. Here we’ve discussed how to choose a beginner camera; for more information, see our guide on how to choose the right camera for your needs.

Choosing a lens
What lens should you buy? There are a number of factors to consider when you choose the best lens for your camera. In this guide we explain camera lenses in detail and how they work. These quick tips for buying a second-hand lens are really true for any optic you want to purchase. Is it compatible with your camera’s mount? Is the focal length suitable for the type of images you want to make? You wouldn’t want a wide-angle lens if wildlife is your subject of choice, for instance.
Buying a new lens is no small purchase, so don’t go making any ill-informed choices. When buying your first lenses you’ll want to consider other factors, such as its speed, or maximum aperture, minimum focus, fixed or floating aperture, optical quality, filter ring, stabilisation, customisation and more. In this guide on what lens is best for your camera, we go into more detail on all of these criteria.
If you need to shoot subjects from afar, we also explain what a telephoto lens is and when and why you might use one. They cost a bit more, but the extra reach you get makes all the difference for certain types of photography. A 70-200mm zoom, in fact, is a useful lens for any photographer to have in their camera bag.
When starting out in photography, beginners often use an 18-55mm optic, or what’s called a ‘standard lens’. These often come bundled in a kit with beginner cameras. A standard lens is great when starting out, as it covers a useful range of focal lengths, but eventually you’ll probably want to broaden your horizons and shoot from different focal lengths. In this guide on how to upgrade from your 18-55mm lens we run through some of the important things to consider.
Depending on where you are in your journey you might be shooting with a full-frame or APS-C-format camera body. This refers to your camera’s sensor size. This adds another consideration to your lens purchasing. In this guide we explain when to use APS-C lenses instead of full-frame and explain what crop factor is to help guide your decision.
Once you’re ready to make your purchase you’ll find no shortage of options on the market. These guides to the best 35mm lenses, best 50mm lenses and best 70-200mm lenses list our favourite options by brand that we’ve tested. Or if you have a specific subject in mind you want to capture, you might find what you’re looking for in our guides to the best macro lenses, best lenses for landscapes, best lenses for portraits or best lenses for wildlife photography.
Understanding your camera & beginner photography techniques
One of the key lessons in photography for beginners is learning how to set up your camera. Understanding which image file formats and quality settings to choose, formatting your memory card and setting copyright information are all among the first things you should do.
From there, the settings you choose largely depend on your subject matter and the light conditions. The guides below will help you ascertain which settings to choose for exposure settings and more:
Image quality settings & shooting modes
- Raw or JPEG: when to use each file format
- What is a raw file in photography?
- What is an anti-aliasing filter?
- What is white balance: how to achieve perfect tones
- How to set your white balance manually
- Drive modes explained: when and how to use them
- What is Aperture Priority mode, and how does it work?
- How to use Bulb mode for stunning long exposures
Exposure
- ISO in Photography: what it is and when to use your higher settings
- When to change your camera’s ISO setting
- Which ISO setting should you use at night?
- How to use exposure bracketing on your camera
- Are shutter speed and aperture the same: a simple guide for beginners
- What is a good exposure in photography?
- What is exposure compensation?
Focusing
- What is back button focusing (and when to use it)?
- Manual focus: 3 modern technologies that make sharp images easier
- How to switch your camera to manual focus
- 3 quick tricks for focusing manually with your camera
- 9 times when autofocus will fail you
- What is depth of field in photography?
- How to get shallow depth of field with any camera
Composition
If you’re feeling really motivated, check out our guide on how to learn photography faster or check out these answers to the most searched photography questions on Google.




